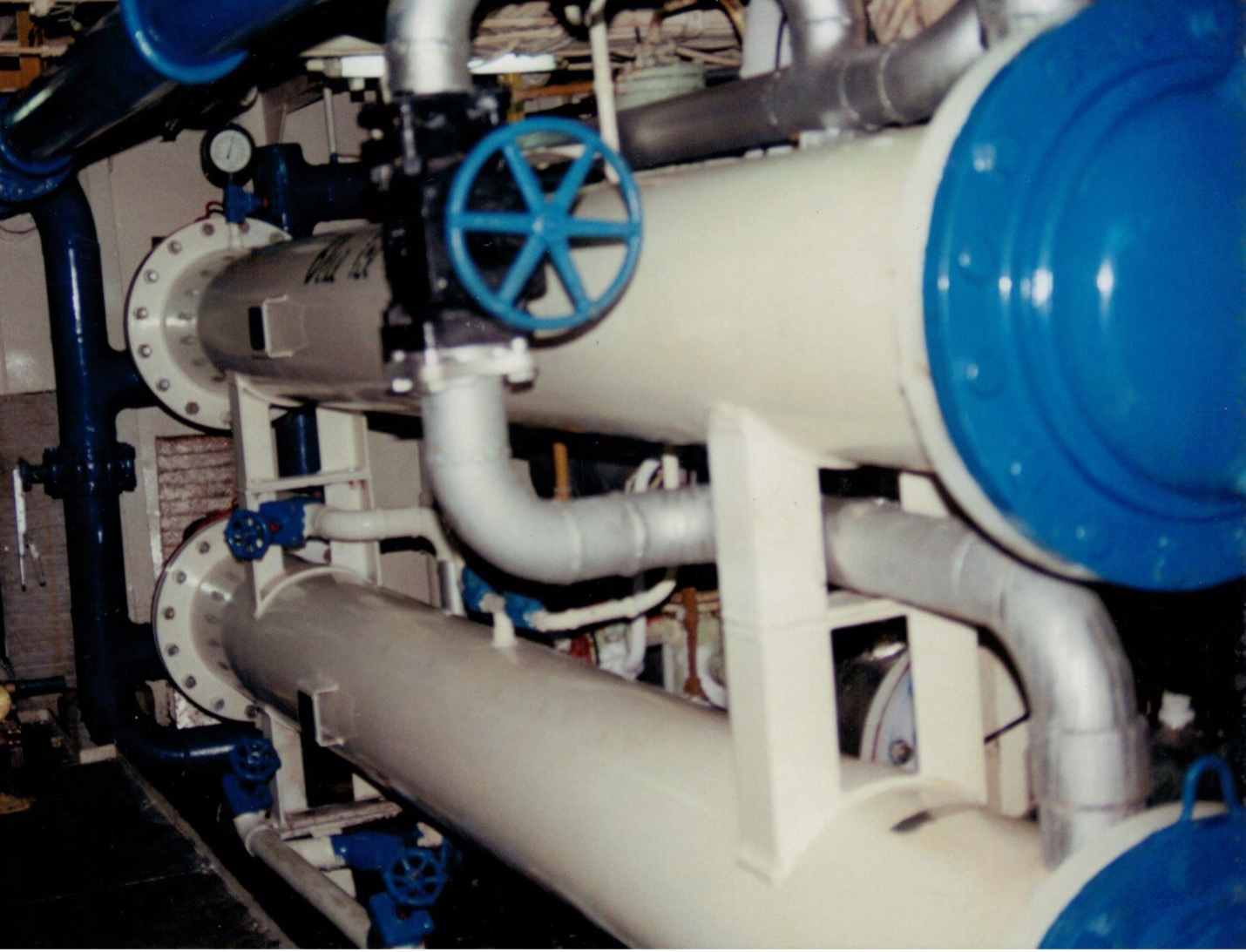
Shell & Tube Marine Heat Exchangers
OUR PRODUCTS
-
Air Conditioning
-
Engine Cooling
-
Exhaust Cooling
-
Machinery Cooling
-
Refrigerated Sea Water
-
Electric Battery Cooling
Titanium Marine Technologies – Marine Heat Exchangers
What are the different types of heat exchangers?
Heat exchangers come in two configurations, Shell & Tube and Plate & Frame. For Sea Water service, the Shell & Tube heat exchanger is the best and most reliable option. They can handle marine growth, debris, silt and sand much better than a Plate & Frame unit. Plate & Frame exchangers tend to plug off with sand, silt and marine growth because the plates are ‘stacked’ in a very tight sandwich with very small passages.
Cleaning a Plate & Frame unit a tedious process and may require an expensive set of new rubber gaskets. Shell & Tube units are easily cleaned with a water lance and do not require new gaskets when they are re-assembled. Cleaning generally takes less time and is contained in small area in the engine room.
Titanium Marine heat exchangers are fully TIG welded and use only Titanium where ever Sea Water is present, including the Sea Water Inlets and Outlets. Corrosion and erosion are not a concern due to the mechanical toughness of Titanium and its chemical properties.
Heat exchangers are used to cool or heat a fluid by passing it through tubes which are surrounded by another colder or warmer fluid. Applications include Engine & Machinery cooling, Air Conditioning Condensers and Refrigerated Sea Water systems. In each case, the heat is exchanged to the sea water and pumped back to the ocean.
Sea Water is corrosive to most metals, except for Titanium. Copper-Nickel, Brass, Stainless and Carbon steel don’t last due to the corrosive and erosive environment.
Mechanically, Titanium is very tough and is the ideal material for all sea water or exhaust gas applications. Call today to learn more about our shell & tube marine heat exchangers!
Other Titanium based product applications
Oil & Fuel coolers: Cooling the fuel and lube oil on a ship extends engine life and maintains performance. Today’s fuel circulation systems require a proper cooling system in order to keep the engine firing properly.
Exhaust Gas Elbows: Environmental pollution is becoming a very important topic in the marine industry. A ship’s air pollution can be reduced by cooling the exhaust gases from the engines and boilers. Cooling the exhaust gases reduces NOx emissions, delivering a lower pollution signature. Capturing the waste heat can often be used for energy needs in the vessel accommodations.
Lithium Battery Cooling: New Hybrid and Battery Electric propulsion systems also create a lot of heat when charging and using Lithium batteries. Specialty Titanium heat exchangers can transfer this heat to the ocean while keeping the batteries cool.
RSW: Refrigerated sea water (RSW) systems use both Flooded or Direct Expansion (DX) chillers for cooling the fish. The “Sales Value of the Catch” is dramatically extended if the fish can be cooled very quickly. Titanium chillers work well in cold brines and won’t plug with fish entrails, scales and fins because large diameter tubes can are used. Both Freon and Ammonia refrigerants are suitable for use with Titanium chillers and condensers.
Specifications:
Titanium Shell & Tube heat exchangers are able to withstand both high pressures and temperatures and vary according to the specific application.
Pressures: Up to 750 psig
Temperaturs: -20F to 500F
Acids: High resistance to all types
Sizes: 4″ dia to 30″ dia
Titanium’s attractive properties and inherent corrosion resistance is due to its adherent protective oxide film that is chemically stable over a wide range of applications, from highly oxidizing to mild conditions. Because of these favorable qualities, Titanium alloys are usually expected to resist most natural water conditions and common salt solutions, chlorides, sulfates, silicates, phosphates, nitrates, carbonates, and others that have a pH range of 3-12. When compared to Stainless Steels, Titanium does not demonstrate the same susceptibility to stress corrosion from chlorides, making the material well suited for seawater, brine applications, and other similar instances.
RSW & FREEZING SYSTEMS
Your diesel main engines and generators need efficient cooling for long service life. Rejecting engine heat to the ocean requires thousands of gallons per hour of sea water flowing through the jacket water and turbo intercoolers. Traditional copper-nickel engine coolers will fail over time and can pump raw sea water INTO the engines and auxiliaries.
This type of failure can cost tens of thousands of dollars and months out of service. With titanium jacket water and turbo intercoolers, you will have the most robust heat exchangers available. Your engines will run cooler and your valuable assets will be protected.
- Smaller, lighter, with longer service life
- Reduce engine jacket water temperatures
- Cooler running for propulsion gearboxes and HPUs
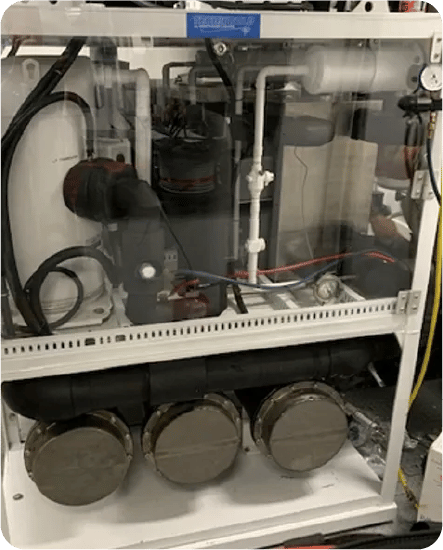
- Eliminates zinc anode maintenance
- All tubes 100% seal welded
